In an abrupt reversal, the bandit cross into the United States is now down severely, according to fresh border numbers. These data, shared recently by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), are revealing valuable information about border enforcement, the effectiveness of policy changes, and global migration trends. But what’s behind this rapid downturn, and how could it shape immigration policy to come?
A Dramatic Drop in Border Apprehensions
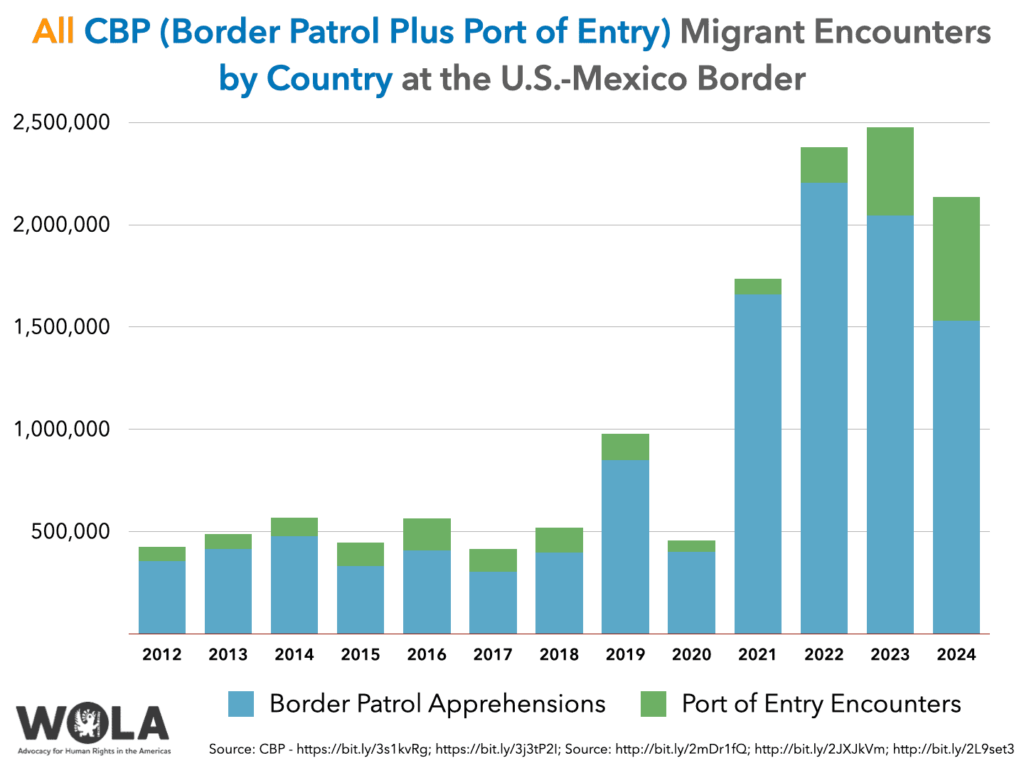
The new figures from CBP are astounding. Unlike for years when illegal immigration at the U.S.-Mexico border was a persistent problem, recent data suggest a major decline in illegal border crossings. Compared to recent years, illegal immigrant apprehensions at the U.S. southern border are down by more than 40% according to the latest statistics released today. This marks a sea change in the course of immigration, which saw record numbers of border encounters in recent years.
At a Glance: Key Border Data
- Total Border Encounters: Total encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border were down 42 percent from 2023 to 2024.
- Apprehensions And Arrests: Border patrol arrests have fallen almost 35%, suggesting a seismic shift in illegal immigration activity.
- Family Units and Unaccompanied Minors: There was a significant decrease of more than 30% in the apprehensions of family units and unaccompanied minors, traditionally considered vulnerable populations.
That sudden decrease in illegal immigration has raised questions about what caused the disruption. Is it policy, economic, or a reflection of changing patterns of migration?
How U.S. Immigration Policies Have Played a Role
The main driver of the recent decline in illegal immigration also seems to be the U.S. government’s policies. Though there’s plenty of ongoing discussion about how effective each measure is, the changes made in recent years have been a big part of reducing unlawful crossings.
How Title 42 and Other Enforcement Actions Have Impacted Access
- Title 42 expulsion policy: Title 42, initially put into place in the pandemic’s early days, allowed for the rapid expulsion of migrants crossing the border. While it faced plenty of criticism, it continued into the Biden administration and remains a cornerstone policy in the Biden administration’s effort to control border security.
- Enhanced Border Surveillance Tech: The United States has increasingly depended on advanced technologies — including drones, sensors, and artificial intelligence — to surveil the border with greater efficiency. These tools have enabled border agents to detect illegal crossings more easily and apprehend violators faster.
- “Remain in Mexico” policy: “Remain in Mexico,” the controversial policy keeping asylum seekers in Mexico while their claims are processed, continues to deter many migrants from crossing the border illegally.
These enforcement methods are rendering it more and more challenging for individuals to gain entry to the U.S. without appropriate documentation. As these numbers illustrate, these policies are having a continued, measurable impact on illegal immigration levels.
International Cooperation & Diplomatic Agreements
A major reason is improved diplomatic relations between the U.S. and surrounding countries. In particular, the United States has collaborated with Mexico and Central American countries to stem the flow of migrants.
Mexico’s Role in Border Enforcement:
Mexico has pledged to boost its border enforcement, including increasing patrols in southern areas and cooperating with American authorities to interdict migrants before they reach the U.S. border.
Central American Cooperation:
Initiatives such as the Central America Minors program, and efforts to create legal pathways for asylum seekers, have reduced the incentive for illegal migration by providing viable options for legal entry into the U.S..
Increased regional cooperation between the United States and its neighbors has enabled the U.S. and those neighbors to better control illegal migration, easing pressure at the southern border.
Economic Factors of Migration — Global
While America’s policies have enormous weight, the global economic environment and conditions elsewhere also weigh heavily on migrations.
Policy Issues: Databases, Economic Conditions in Source Countries
Most of those attempting to cross illegally from the south are from Central America, Mexico, and other areas where economic distress exists. But changing economics have shifted the migration calculus.
- Inflation and Economic Decline: Many of the countries sending migrants to the U.S. have experienced economic downturns, rising inflation, and widespread unemployment. That has made it more expensive for people to make the trip, meaning fewer people are trying to make it across the border.
- Better conditions in Mexico: Certain regions of Mexico have found economic growth, particularly in industrial areas so, job creation has increased and living standards have improved. As a result, not as many people are looking to leave Mexico in search of U.S. opportunities.
- Local Solutions to Migration: In several Central American countries, including Guatemala and Honduras, local development programs focused on reducing poverty and creating jobs are being introduced. These efforts have helped to deter some would-be migrants from attempting a dangerous journey northward.
The Impact of Global Crises and Disasters
And while economic improvements in some areas are welcomed, other places have been rocked by political upheaval, violence, and natural disasters that have increased migratory pressures.
- Climate Change and Natural Disasters: Thousands of people have been displaced in countries including Honduras, Guatemala, and El Salvador due to hurricane seasons, droughts, and floods. Many of those still try to cross the border into the U.S., even as illegal immigration overall has dropped.
- Escalating Global Political Unrest: Political instability, most notably the humanitarian disasters in Venezuela, Nicaragua, and elsewhere, continue to fuel migration. But these factors have not had the same overpowering influence that they have in previous years.
These international variables remain determinants of migration patterns and contribute to variations in the number of irregular crossings.
The Role of Smuggling and Cartels
Even though border enforcement and economic issues have all contributed to a slowdown of illegal immigration, it should not be forgotten that crime syndicates involved in human and drug trafficking and smuggling gray and white goods continue their work. These organizations remain in operation, but the combination of fortified borders and ramped-up law enforcement collaboration have hampered their activities.
Smuggling Networks Changing with New Security Arrangements
Smuggling groups, in turn, are adjusting both their tactics and technologies to counter such security adaptations. For example:
- New Arteries and Approaches: Since border security has gotten tighter in traditional crossing areas, smugglers are finding new arteries and approaches to aid people in crossing the border. These include tunnels, concealed compartments in vehicles and offshore routes.
- Increased Penalties for Smugglers: U.S. and Mexican officials have targeted smugglers, leading to higher arrest rates for trafficking groups. While the risk has discouraged some potential smugglers, others are still operating in the shadows.
Despite these adjustments, one area for concern are smuggling and human trafficking networks. The drop in illegal immigration isn’t a sign that these criminal enterprises have been eradicated but that law enforcement has become more efficient in neutralizing them.
The Long-Term Impacts of Declining Illegal Immigration
This steep decline of illegal immigration comes with both positive and negative implications for the U.S. and its immigration policy in the future.
Coming Down on Legal Immigration
As illegal immigration is falling, a spotlight is increasingly falling on the legal immigration system. A focus on expanding temporary work visas, enhancing asylum processing, and creating pathways for undocumented people to achieve legal status could further help to reduce the need for illegal crossings.
The Border Security Budget Adjustments
With illegal immigration now down, there likely will be demands to reduce the federal border security budget. But many experts who study international migration caution that right security is needed to respond to the changing nature of global migration, despite a declining number of illegal crossings.
On International Diplomacy and Migration Solutions
The United States will have to keep working with its neighbors to keep migration manageable. The next president will have to be a partner, and you’ll need to have strong diplomatic relations with countries such as Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras in order to address the causes of migration, and to sustain cooperation on enforcing borders going forward.
A Complex and Fluid Situation
The drastic drop-off in illegal immigration is, no doubt, a good thing for the U.S., but it is also a complicated and dynamic situation. Although policy changes, enhanced border security, and a shift in the global economy have played parts in that decline, future hurdles lie ahead. Besides global instability, immigration through illegal channels and the access slide needs vigilance as well in the “quest” for better security and compassionate immigration processes that are flexible.
FAQs
1. What are the two main reasons for the decrease in illegal immigration?
The reasons are stronger enforcement policies, better U.S.-Mexico coordination, shifts in economies in the countries that source many migrants and new technologies for securing the border.
2. Can we expect this drop in illegal immigration to last?
Though the decrease is dramatic, new variables — including global instability, political shifts, and future crises — all could affect immigration trends, and in particular lead to rises in illegal crossings again.
3. How is U.S. border enforcement evolving to meet new challenges?
The U.S. is increasingly turning to advanced technologies such as drones, surveillance systems, and artificial intelligence to monitor borders more effectively. Diplomatic efforts with neighboring countries have also strengthened enforcement.
4. What does this mean for U.S. immigration policy?
Less illegal immigration may create opportunities for legally-oriented immigration work — such as work visas or asylum case processing — while keeping **border






